
Environment & Resources
Humanity's use of natural resources is pushing the planet to its limits. At the same time, our customers increasingly expect more from our products, packaging and processes in terms of their environmental compatibility.
For a world worth living in – today and tomorrow – we strive to reduce the environmental impact of our business activities and make a positive contribution to protecting the environment. Our ambition is to take on a leading role in resource conservation in our industry. As we move toward that goal, we are also guided by the environmental principles of the Global Compact which we have signed.
To live up to our aims, we are careful to conserve the raw materials we need to produce our products. We make certain that environmental requirements are defined for each segment of the product life cycle early on during the development process. We also take care to ensure environmentally responsible sourcing and efficient energy use, and we are increasingly turning to sustainable sources for our raw materials. Last but not least, the high quality of our products helps guarantee that they enjoy a long lifespan, which also contributes to conserving resources.
Efficient use of resources is also an area of focus for us in our work with packaging and consumables. In line with the concept of the circular economy, we concentrate specifically on ensuring that the materials we use can be reused, thereby preventing unnecessary waste.
Environmental management certification
Our goal is to minimize the potential negative impact of our business activities on the environment. The framework for our environmental actions as a company is the Eppendorf Environmental & Safety Mission, which applies throughout the company. It stipulates that measures to reduce and prevent environmental impact should be identified, implemented and improved on an ongoing basis. We achieve this goal through our certified environmental activities based on the ISO 14001 standard. Our environmental management system allows us to achieve systematic improvement in our environmental performance and manage change processes effectively.
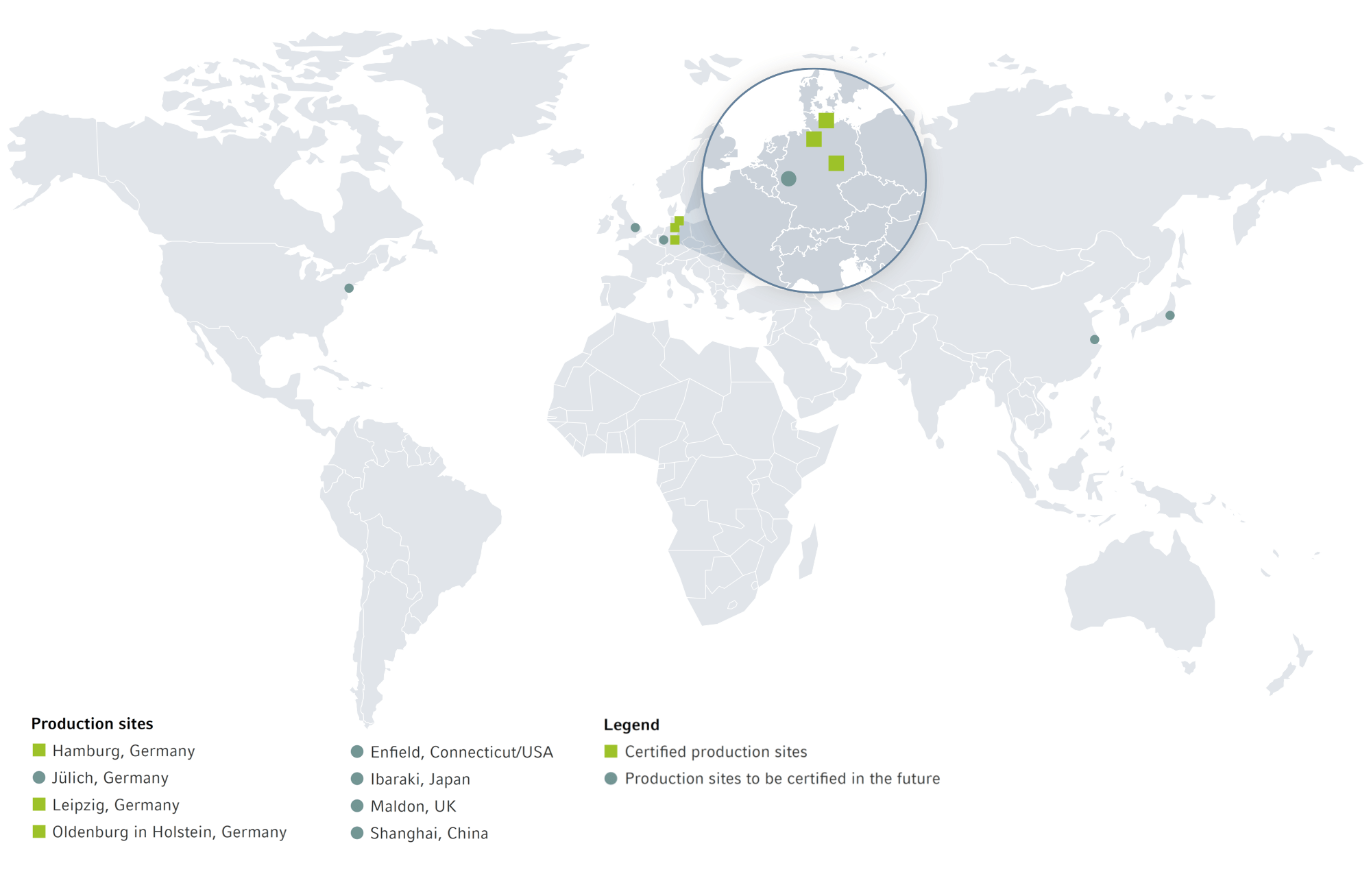
ISO 14001 certification for specific locations
By the end of 2021, 45% of our production locations around the world held the ISO 14001 environmental management certification. Five entities in Germany have had environmental management certification since 2013. Further sites are to be added in the years to come; a certification strategy that maps out these actions was adopted by the Management Board in 2021. Two further entities, one in Germany and one in the USA, are to receive certification in 2022.
Performance indicators
As part of our annual ISO 14001 management review, we identify, analyze and evaluate various performance indicators such as total waste volume and waste volume in relation to production output. In the process, we distinguish between performance indicators that apply company-wide and those that relate to specific sites. Over the course of our successive ISO 14001 location certifications, we develop standardized reporting for these key indicators. We also analyze financial indicators to study the cost-effectiveness of the measures we have put in place.
ISO 14001 Certified Production Sites of the Eppendorf Group
Download(PNG, 105 KB)
Organization
The Management Board and the managing directors who are in charge of the operational business are responsible for environmental management. The Management Board makes all strategic decisions and confirms operational projects and objectives within the scope of the ISO 14001 management review. Depending on the project and location, operational implementation is handled by the local health, safety and environment (HSE) managers in cooperation with global specialists, facility managers, operations managers and/or additional specialists.
Raising awareness among employees
Every year, the Eppendorf Academy offers online training courses on environmental topics and environmental management at Eppendorf, which all employees of the Hamburg and Oldenburg locations are required to complete. There are plans to add yearly training on environmental topics at other locations in the future.
Standards & guidelines
The main rules that apply to us in Germany are the stipulations of the German Circular Economy Act, Commercial Waste Ordinance, Packaging Act and Electrical and Electronic Equipment Act, along with the EU Waste Framework Directive. International waste laws for sites outside Germany have not been documented systematically at this time. In the future, we will observe international waste laws and further areas of law within the scope of our ISO 14001 certification.
Additional guidance is provided by our company-wide HSE Mission, which is accessible to all employees in German and English on the intranet. It sets out our mission, ambitions and pledges relating to environmental protection and the fields of safety and health.

Ecological commitment & involvement: pitching in to help
2021 marked the fourth time that Eppendorf participated in an initiative called “Wi mook dat!” (We can do it!). The goal is to get companies in Hamburg involved in social and ecological causes. As in years past, participating Eppendorf employees also supported the “Living Alster” project, crafting structures out of wood, gravel and debris to control the flow of water and create valuable habitats for fish, small animals, kingfishers and otters.
Waste & recycling
At Eppendorf, waste arises at every stage of the value chain. Waste includes not just household waste, wastewater and industrial waste, but also hazardous materials originating in medical and electronic products. Our goal is to prevent waste to the greatest possible extent and reduce it where prevention is not possible. One of our strategic areas of focus is reducing the share of fossil primary plastics used in our overall production operations through measures such as new and more efficient product construction.
Waste prevention & reduction
Waste prevention and reduction are highly important to Eppendorf, due in large part to our customers’ increasingly stringent requirements. This is why our materiality analysis has identified related topics as being of high strategic importance. Our activities in this area focus on three aspects. First, we aim to minimize resource consumption and the waste arising from our own marketing materials and transportation packaging. A further goal is to reduce the waste arising at our customers’ end through the use of our consumables as well as from the packaging of our products excluding consumables.
We also strive to optimize our process and plant engineering in such a way as to prevent waste and reuse valuable raw materials. For example, we adapt processes to minimize production scrap and use a recycling method at the Leipzig location to separate and reuse cooling lubricants and aluminum shavings.
Data for sustainability controlling under development
Site-specific waste reduction targets are set in each case as part of our ISO 14001 certification. We launched a project to capture waste data across all production sites in 2021. Going forward, the goal is to use these data as part of a resource strategy which will apply worldwide, as well as to further enhance our internal sustainability controlling structures and activities. The key indicators will be disclosed as part of our sustainability reporting in the future.
Structured waste management
At Eppendorf, waste management is a part of our environmental management activities. Local HSE managers or site waste managers are responsible for these aspects at individual locations.
We have defined a company-wide standard for the handling of waste. The standard stipulates that waste must be collected separately by specific categories and provided to waste disposal entities in suitable containers. All waste must be classified and logged in a waste record. Hazardous waste is labeled separately, and records of disposal are kept. The standard also stipulates that only specialized waste disposal companies can be used and commissioned for disposal purposes.
In line with these specifications, disposal is handled at all German sites by specialized partners selected by Eppendorf. The disposal companies provide waste balance sheets. At the Hamburg site, an external service provider also handles internal collection and rough pre-sorting of waste. The disposal processes are monitored each year under our certified environmental management system.
At 76 %, the reuse and recycling rate of our waste is high. Even with positive site development and increased production volume during the year under review, our waste volumes and energy efficiency have remained relatively stable in 2021.
Reusing aluminum waste
Aluminum is an important material at Eppendorf. Aluminum dust is created during processing. The particles are contained in cooling lubricant used to protect our equipment against high temperatures. To be able to reuse both the aluminum dust and the cooling lubricant as it emerges from the cycle, we introduced an innovative recycling method at the Leipzig site in 2013. The aluminum particles are captured and passed through a hydraulic press, which compacts the material at high pressure into small briquettes that can then be reused. This compacting procedure also releases a large portion of the lubricant that is used for cooling, meaning that it can also be reused. As a result, this method has both ecological and economic benefits.
Paper use within the company
In recent years, we have shifted our paper documentation to digital systems across many areas. We also increasingly communicate via digital channels, internally and externally, which has allowed us to significantly reduce our use of paper and toner.
Beyond that, we are careful to prevent unnecessary waste at our offices and logistics centers. All offices at our central location in Hamburg have been equipped with paper recycling bins since 2005.
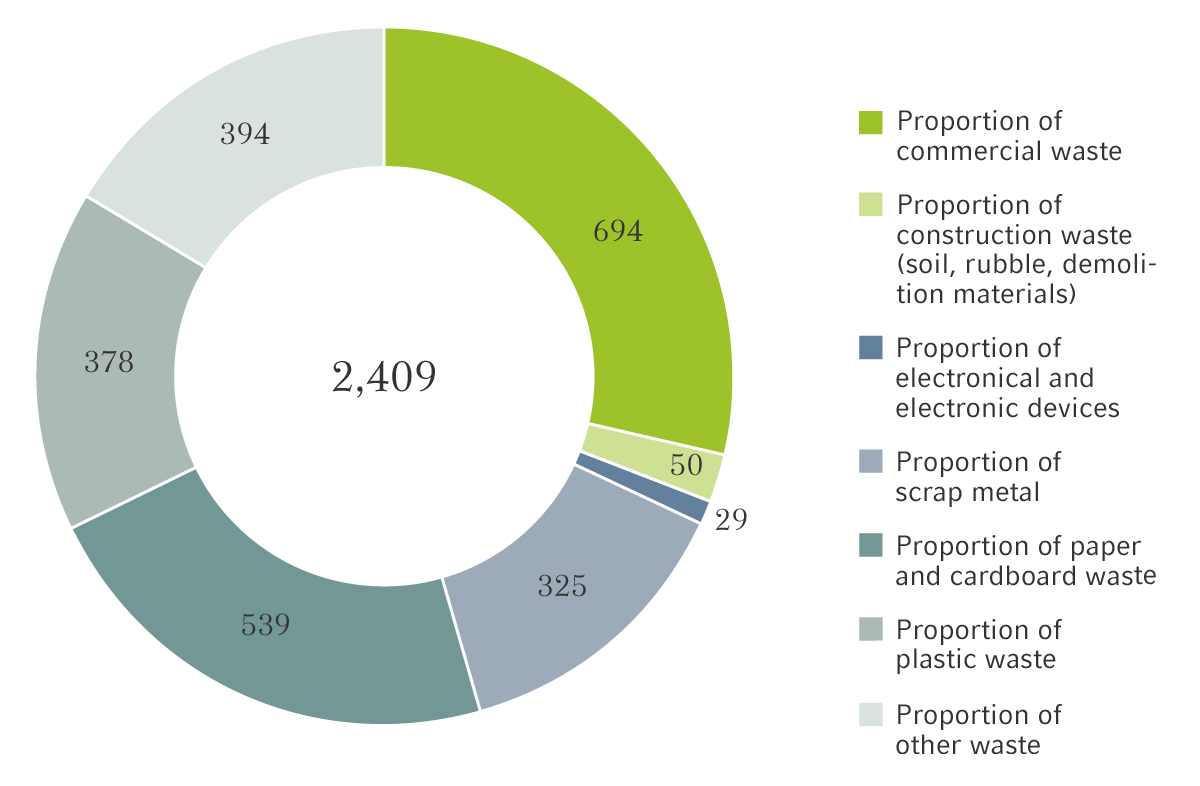
Total waste by category in t
GRI 306-3
(PNG, 28 KB)
Consumables at our customers’ end
Whereas in the past, biomedical research laboratories used almost exclusively glass-based vessels, these days, the majority of laboratory vessels is made from single-use plastic. These items have significant advantages over glass in terms of manufacturing costs, ruggedness and purity. In addition, many experiments are now conducted at the microliter or nanoliter scale. This requires vessels and tips with ultra-small dimensions, which either cannot be manufactured out of glass, or which would be prohibitively expensive to produce. Instead, these single-use items are made of polypropylenepolypropylenePolypropylene is a commonly used type of plastic. It is odorless, skin-friendly and suitable for food and pharmaceutical applications. granulate, which is based on fossil raw materials.
Optimizing consumables & researching alternatives
We aim to reduce the use of materials. One way to achieve this is through the optimization of wall thickness and dimensions of our consumables. However, we are constrained in these efforts by both the necessary mechanical and chemical stability of the products and the production conditions. Another issue is that the dimensions of vessels and plates are often based on international standards for size, with precisely defined inserts. As things currently stand, we have optimized our consumables with regard to wall thickness and dimensions.
Our development departments have also been hard at work researching the use of bio-based raw materials for plastic applications. In addition, we are experimenting with the use of recycled materialsrecycled materialsRecyclates are so-called secondary raw materials obtained from the recycling of plastic waste and used to manufacture new products. for the production of single-use items. However, there are limits to what can be realistically achieved. For example, recycled materials can currently not be used for single-use items that come into direct contact with samples. Standard recycled materials may contain substances which could leach out of the plastic upon contact with liquids. These leachables will then contaminate the sample material inside the pipette tip or sample tube.
Preventing & recycling waste within customers’ operations
One key aspect of our efforts to protect and conserve resources is reducing the plastic waste generated in our customers’ operations. The challenge is that this plastic is often contaminated with biological or chemical substances or radiation, making it potentially harmful to human health and the environment. Plastic-based laboratory waste that has come into direct contact with samples is typically incinerated. Recycling is either impossible or prohibitively expensive with the technologies currently available. In some cases, incineration of laboratory waste is also required by law.
However, our single-use items also contain plastic elements that do not come in direct contact with sample materials, including holders for pipette tips, storage boxes for tips inside these holders and external packaging for the consumable items. Eppendorf considers these to be auxiliary products, which enable the correct use of the products themselves. Depending on how these items are used in the laboratory, they may be classified as non-contaminated waste. We urge our customers to separate product packaging and auxiliary products as much as possible prior to moving the items into the laboratory where they may come into contact with sample material or contaminated work surfaces. Sorting at this early stage may allow recycling of certain plastic elements.
Designing packaging efficiently
Wherever possible, we avoid unnecessary use of materials for our packaging and reduce package sizes and material thickness. We are also always looking for sustainable alternative packaging materials.
Common types of packaging at Eppendorf:
Primary packaging such as holder systems or boxes for pipette tips is frequently associated with the product itself, as many product characteristics, such as sterility, apply only in combination with the primary packaging.
Product packaging is the term used for the volume of materials surrounding the product during the phase between the final stage of production and the customer-specific use in the laboratory. Depending on the product type and weight, cardboard packages of varying thickness are used.
Transportation packaging is the name we use for specific outer packages that hold multiple products of the same kind and their product packaging. Transportation packaging is designed for efficient, secure shipping. It consists primarily of cardboard with a high percentage of recycled fiber.
Returnable packaging, also known as reusable packaging, is used at various Eppendorf plants to procure component assemblies or parts from suppliers. We send the packaging back to the supplier after the components inside it have been used. Our use of returnable packaging is limited to regional suppliers, as the cost of returning empty packaging to the supplier would otherwise outweigh the savings on materials.
Over the years, we have developed various systems for designing packaging more efficiently or eliminating it altogether. For example, we introduced refill systems for pipette tips back in 2002. These reusable boxes can be sterilized and refilled up to one hundred times. Innovative disposable filter tip holder systems have also been in use since 2021, allowing us to reduce the amount of polypropylene used in holder systems by up to 35%, depending on the tip size. Beyond that, we are always looking for alternative materials for primary packaging.
When it comes to product packaging made of cardboard, we take care to ensure that an increasing proportion of recycled material is used. Depending on the product category, the current proportion is between 70 and 100%. Some product packages have already been designed to use no plastic at all. Cardboard-based holders provide adequate protection for these products. We plan to ramp up our efforts to use these types of packaging in the future.
In principle, we recommend that our customers collect packaging on site and separate product and transportation packaging from that actual products before they reach the laboratory so that they can be recycled without concern for contamination.
Rethinking marketing materials
At Eppendorf, our marketing materials include paper-based brochures, magazines, catalogs and sample packages containing single-use or promotional items. All of our paper marketing documents can be recycled using standard methods. We reduce our use of paper-based documents wherever possible. The COVID-19 pandemic and the social distancing requirements associated with it have also spurred the further digitalization of our marketing materials.
Although we continue to use paper products, we strive to design them as efficiently as possible. For example, our product catalog features more and more products each year, but its weight and volume have remained relatively constant thanks to smaller fonts, thinner paper and the inclusion of QR codes for users to read further information online. Climate-neutral printing and certified paper have also reduced the catalog’s carbon footprint. In addition, many customers use the Eppendorf product catalog for years as a reference work in their laboratories. When disposed of properly, it can be returned into the normal paper recycling process; in addition it is also available in digital format.
We switched to sending out newsletters exclusively via e-mail several years ago. Recipients still have the option of requesting printed versions of our product brochures. To conserve resources in the form of energy and materials, we rely on demand-driven printing for our brochures and flyers. Prior to printing, we conduct regional surveys to determine how many copies will be needed. Our brochures are printed in Hamburg. The paper used is 100% certified virgin fiber. Plans call for a shift to 100% recycled paper in 2022; we also plan to reduce the print run significantly.
Eppendorf publishes magazines on overarching laboratory-related topics twice a year. These magazines include our BioNews and Off the Bench titles. Both publications are printed on a climate-neutral basis and are also available online.
